change readme
This commit is contained in:
parent
1e9a03bc50
commit
11274864ab
1 changed files with 6 additions and 98 deletions
104
README.md
104
README.md
|
|
@ -1,100 +1,8 @@
|
|||
# hoverboard-firmware-hack
|
||||
# hoverboard-firmware-hack-serial-esc
|
||||
|
||||
 
|
||||
 
|
||||
This repo contains an optimized version of the hoverboard mainboard firmware by rene-dev, crinq and NiklasFauth to use as a basic dual ESC.
|
||||
The control logic would be on a separate controller.
|
||||
Motor speed can be send via serial.
|
||||
Optimizations lie in a strict timeout, such that if the connection breaks, is delayed or wrong values are send the motors stop turning until the board is reset.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This repo contains open source firmware for generic Hoverboard Mainboards.
|
||||
The firmware you can find here allows you to use your Hoverboard Hardware (like the Mainboard, Motors and Battery) for cool projects like driving armchairs, person-tracking transportation robots and every other application you can imagine that requires controlling the Motors.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want an overview of what you can do with this firmware, here is a ~40min video of a talk about this project:
|
||||
https://media.ccc.de/v/gpn18-95-howto-moving-objects
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Build Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
Here are detailed build instructions for some finished projects.
|
||||
If possible, a prebuild firmware release is available for these usecases, so you don't need to compile the firmware yourself
|
||||
|
||||
TranspOtter: https://github.com/NiklasFauth/hoverboard-firmware-hack/wiki/Build-Instruction:-TranspOtter
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Hardware
|
||||
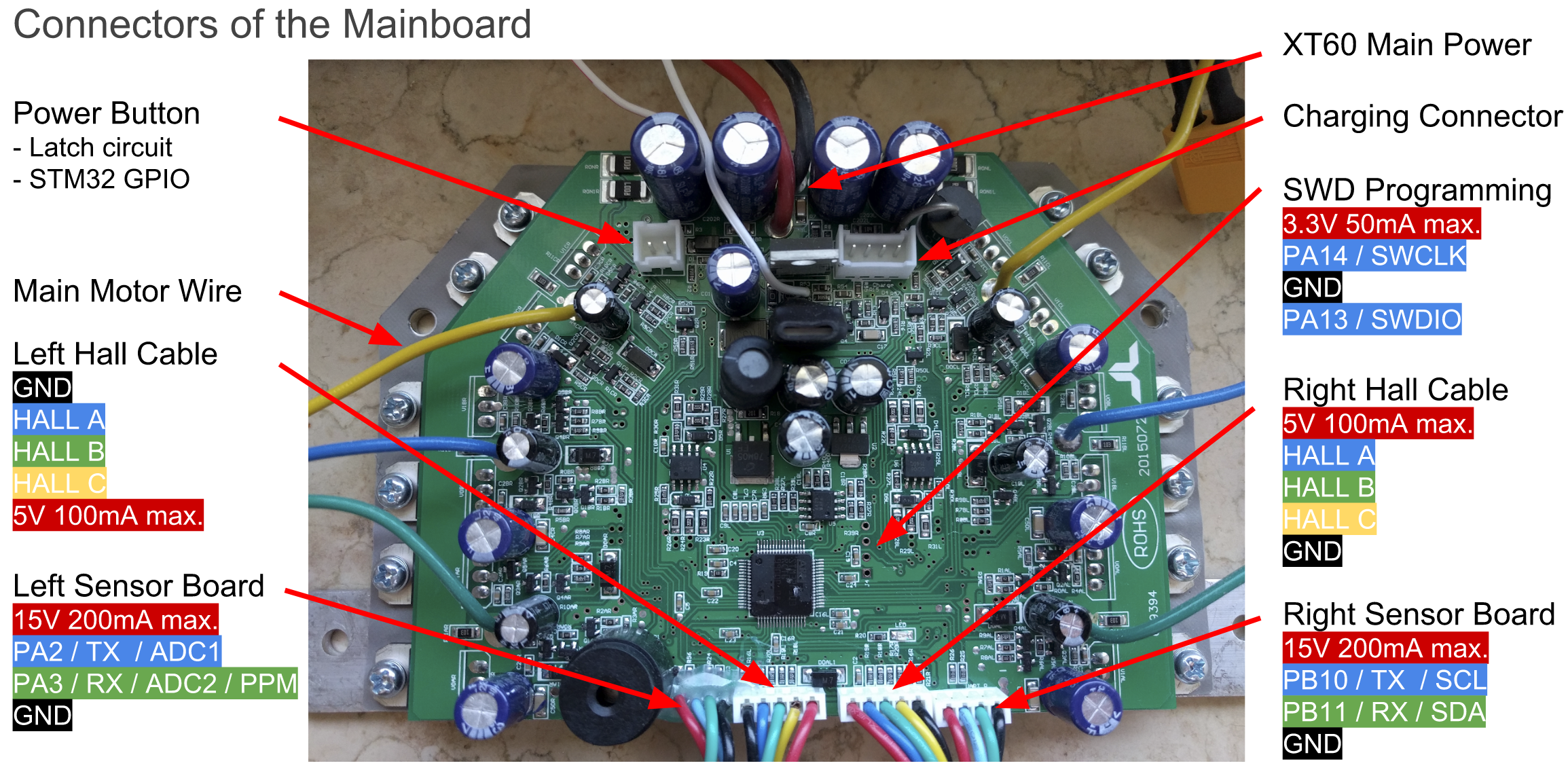
|
||||
|
||||
The original Hardware supports two 4-pin cables that originally were connected to the two sensor boards. They break out GND, 12/15V and USART2&3 of the Hoverboard mainboard.
|
||||
Both USART2 & 3 can be used for UART and I2C, PA2&3 can be used as 12bit ADCs.
|
||||
|
||||
The reverse-engineered schematics of the mainboard can be found here:
|
||||
http://vocke.tv/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=20150722_hoverboard_sch.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Flashing
|
||||
To build the firmware, just type "make". Make sure you have specified your gcc-arm-none-eabi binary location in the Makefile ("PREFIX = ...") (version 7 works, there is a version that does not!) (if the ons in linux repos do not work, use the official version: https://developer.arm.com/open-source/gnu-toolchain/gnu-rm/downloads). Right to the STM32, there is a debugging header with GND, 3V3, SWDIO and SWCLK. Connect GND, SWDIO and SWCLK to your SWD programmer, like the ST-Link found on many STM devboards.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not power the mainboard from the 3.3V of your programmer! This has already killed multiple mainboards.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you hold the powerbutton or connect a jumper to the power button pins while flashing the firmware, as the STM might release the power latch and switches itself off during flashing. Battery > 36V have to be connected while flashing.
|
||||
|
||||
To flash the STM32, use the ST-Flash utility (https://github.com/texane/stlink).
|
||||
|
||||
If you never flashed your mainboard before, the STM is probably locked. To unlock the flash, use the following OpenOCD command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm32f1x.cfg -c init -c "reset halt" -c "stm32f1x unlock 0"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If that does not work:
|
||||
```
|
||||
openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm32f1x.cfg -c init -c "reset halt" -c "mww 0x40022004 0x45670123" -c "mww 0x40022004 0xCDEF89AB" -c "mww 0x40022008 0x45670123" -c "mww 0x40022008 0xCDEF89AB" -c "mww 0x40022010 0x220" -c "mww 0x40022010 0x260" -c "sleep 100" -c "mww 0x40022010 0x230" -c "mwh 0x1ffff800 0x5AA5" -c "sleep 1000" -c "mww 0x40022010 0x2220" -c "sleep 100" -c "mdw 0x40022010" -c "mdw 0x4002201c" -c "mdw 0x1ffff800" -c targets -c "halt" -c "stm32f1x unlock 0"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm32f1x.cfg -c init -c "reset halt" -c "mww 0x40022004 0x45670123" -c "mww 0x40022004 0xCDEF89AB" -c "mww 0x40022008 0x45670123" -c "mww 0x40022008 0xCDEF89AB" -c targets -c "halt" -c "stm32f1x unlock 0"
|
||||
```
|
||||
Or use the Windows ST-Link utility.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can simply flash the firmware:
|
||||
```
|
||||
st-flash --reset write build/hover.bin 0x8000000
|
||||
```
|
||||
or
|
||||
```
|
||||
openocd -f interface/stlink-v2.cfg -f target/stm32f1x.cfg -c flash "write_image erase build/hover.bin 0x8000000"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
First, check that power is connected and voltage is >36V while flashing.
|
||||
If the board draws more than 100mA in idle, it's probably broken.
|
||||
|
||||
If the motors do something, but don't rotate smooth and quietly, try to use an alternative phase mapping. Usually, color-correct mapping (blue to blue, green to green, yellow to yellow) works fine. However, some hoverboards have a different layout then others, and this might be the reason your motor isn't spinning.
|
||||
|
||||
Nunchuck not working: Use the right one of the 2 types of nunchucks. Use i2c pullups.
|
||||
|
||||
Nunchuck or PPM working bad: The i2c bus and PPM signal are very sensitive to emv distortions of the motor controller. They get stronger the faster you are. Keep cables short, use shielded cable, use ferrits, stabilize voltage in nunchuck or reviever, add i2c pullups. To many errors leads to very high accelerations which triggers the protection board within the battery to shut everything down.
|
||||
|
||||
Most robust way for input is to use the ADC and potis. It works well even on 1m unshielded cable. Solder ~100k Ohm resistors between ADC-inputs and gnd directly on the mainboard. Use potis as pullups to 3.3V.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
|
||||
Have a look at the config.h in the Inc directory. That's where you configure to firmware to match your project.
|
||||
Currently supported: Wii Nunchuck, analog potentiometer and PPM-Sum signal from a RC remote.
|
||||
A good example of control via UART, eg. from an Arduino or raspberryPi, can be found here:
|
||||
https://github.com/p-h-a-i-l/hoverboard-firmware-hack
|
||||
|
||||
If you need additional features like a boost button, have a look at the while(1) loop in the main.c
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional Hardware
|
||||
|
||||
* [breakout/interconnect boards](https://github.com/Jan--Henrik/hoverboard-breakout) Breakout/Interconnection boards for hoverboard hacking.
|
||||
|
||||
### Projects based on it
|
||||
* [bobbycar-optimized firmware](https://github.com/larsmm/hoverboard-firmware-hack-bbcar) based on this one with driving modes, acceleration ramps and some other features
|
||||
* [wheel chair](https://github.com/Lahorde/steer_speed_ctrl) controlled with a joystick or using a CC2650 sensortag to control it over bluetooth with pitch/roll.
|
||||
* [TranspOtterNG](https://github.com/Jan--Henrik/transpOtterNG) TranspOtter is an open source semi self driving transportation platform based on hoverboard hardware
|
||||
* [BiPropellant](https://github.com/bipropellant) - fork which focusses on reliable machine control, but also retains HoverBoard functionality if desired.
|
||||
This firmware is for example used in my "hoverbrett" testplatform: https://figch.de/index.php?nav=hoverbrett
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Reference in a new issue